Retained Earnings Formula: Explanation and Examples

Distribution of dividends to shareholders can be in the form of cash or stock. Cash dividends represent a cash outflow and are recorded as reductions in the cash account. These reduce the size of a company’s balance sheet and asset value as the company no longer owns part of its liquid assets. Then, identify the total dividends paid to shareholders, which can be found on the income statement below the earnings per share (EPS) data and details on the cash ending re formula flow statement in the cash from financing section. To accurately compute retained earnings, which reflect a company’s accumulated profit after dividends, one must understand its components and the formula used for calculation. Retained earnings are crucial for investors assessing the company’s financial health and growth potential.
- The statement of shareholders’ equity will include the changes in these earnings for a specific period.
- Upon combining the three line items, we arrive at the end-of-period balance – for instance, Year 0’s ending balance is $240m.
- Factors such as an increase or decrease in net income and incurrence of net loss will pave the way to either business profitability or deficit.
- And while that seems like a lot to have available during your accounting cycles, it’s not.
- The POWER function is particularly useful when dealing with exponential calculations like CAGR.
Step 3 of 3

Management and investors can use retained earnings to assess whether a company is reinvesting enough for future growth or returning enough to shareholders. A retention ratio of 75% implies that Company D reinvests three-quarters of its net income into the business, which can lead to significant growth in retained earnings over time. Retained earnings (RE) is the cumulative net income that has not been paid out as dividends but instead has been reinvested in the business.
- Retained earnings also provide your business with a cushion against any economic downturn and give you the requisite support required to sail through depression.
- If the company suffered a loss last year, then its beginning period RE will start with a negative.
- Dividends are always subtracted from RE because once dividends are declared, the company owes its shareholders the funds and must take these funds out of its retained earnings even if they are simply declared and not paid.
- This can make a business more appealing to investors who are seeking long-term value and a return on their investment.
- Now, you must remember that stock dividends do not result in the outflow of cash, in fact, what the company gives to its shareholders is an increased number of shares.
Example of Retained Earnings Calculation

These tips can help you turn Excel from a simple spreadsheet tool into a powerful data analysis assistant, saving you time and improving accuracy. By staying vigilant and taking the time to review your work, you can avoid these pitfalls and ensure your calculations are reliable and accurate. It’s worth noting that while CAGR is a powerful tool, it’s not the only metric you should rely on.
Additional Excel Tips for Better Performance
You’re just figuring out how much you’ve earned that you haven’t paid out to your shareholders as dividend payments. The figure may be positive or negative, depending upon inputs in the formula. If the company suffered a loss last year, then its beginning period RE will start with a negative. As such, some firms debited contingency losses to the appropriation and did not report them on the income statement. A company’s management team always makes careful and judicious decisions when it comes to dividends and retained earnings.
Always consider other factors like market conditions, investment risk, and personal financial goals when making decisions. If not, don’t worry—just go back and see if there’s a typo or a miscalculation somewhere. Retained earnings provide a source to hire additional sales representatives.
Retention Ratios and Retained Earnings Growth
The level of retained earnings can guide businesses in making important investment decisions. If retained earnings are low, it may be wiser to hold onto the funds and use them as a financial cushion in case of unforeseen expenses or cash flow contra asset account issues rather than distributing them as dividends. However, if both the net profit and retained earnings are substantial, it may be time to consider investing in expanding the business with new equipment, facilities, or other growth opportunities.

11 Financial may only transact business in those states in which it is registered, or qualifies for an exemption or exclusion from registration requirements. 11 Financial’s website is limited to the dissemination of general information pertaining to its advisory services, together with access to additional investment-related information, publications, and links. It generally limits the use of the prior period adjustment to the correction of errors that occurred in earlier years.
Normally, these funds are used for working capital and fixed asset purchases (capital expenditures) or allotted for paying off debt obligations. Retained earnings offer valuable insights into a company’s financial health and future prospects. When a business earns a surplus Certified Bookkeeper income, it can either distribute the surplus as dividends to shareholders or reinvest the balance as retained earnings. Understanding retained earnings is essential for anyone involved in business. Lower retained earnings can indicate that a company is more mature, and has limited opportunities for further growth, but this isn’t necessarily a negative.
- For example, if your retention ratio is 25%, then your dividend payout ratio is 75%.
- After adding/subtracting the current period’s net profit/loss to/from the beginning period retained earnings, you’ll need to subtract the cash and stock dividends paid by the company during the year.
- If a company has no strong growth opportunities, investors would likely prefer to receive a dividend.
- Calculating retained earnings aids in financing the launch of new products.
- This gives you the amount of profits that have been reinvested back into the business.
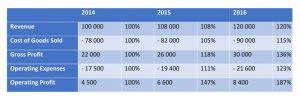
Retained earnings represent a useful link between the income statement and the balance sheet, as they are recorded under shareholders’ equity, which connects the two statements. The purpose of retaining these earnings can be varied and includes buying new equipment and machines, spending on research and development, or other activities that could potentially generate growth for the company. This reinvestment into the company aims to achieve even more earnings in the future. A company’s retained earnings balance can be found on the shareholder’s equity section of the balance sheet (one of the 3 core financial statements), which can be found in the company’s annual report or website. These earnings are considered “retained” because they have not been distributed to shareholders as dividends but have instead been kept by the company for future use.
