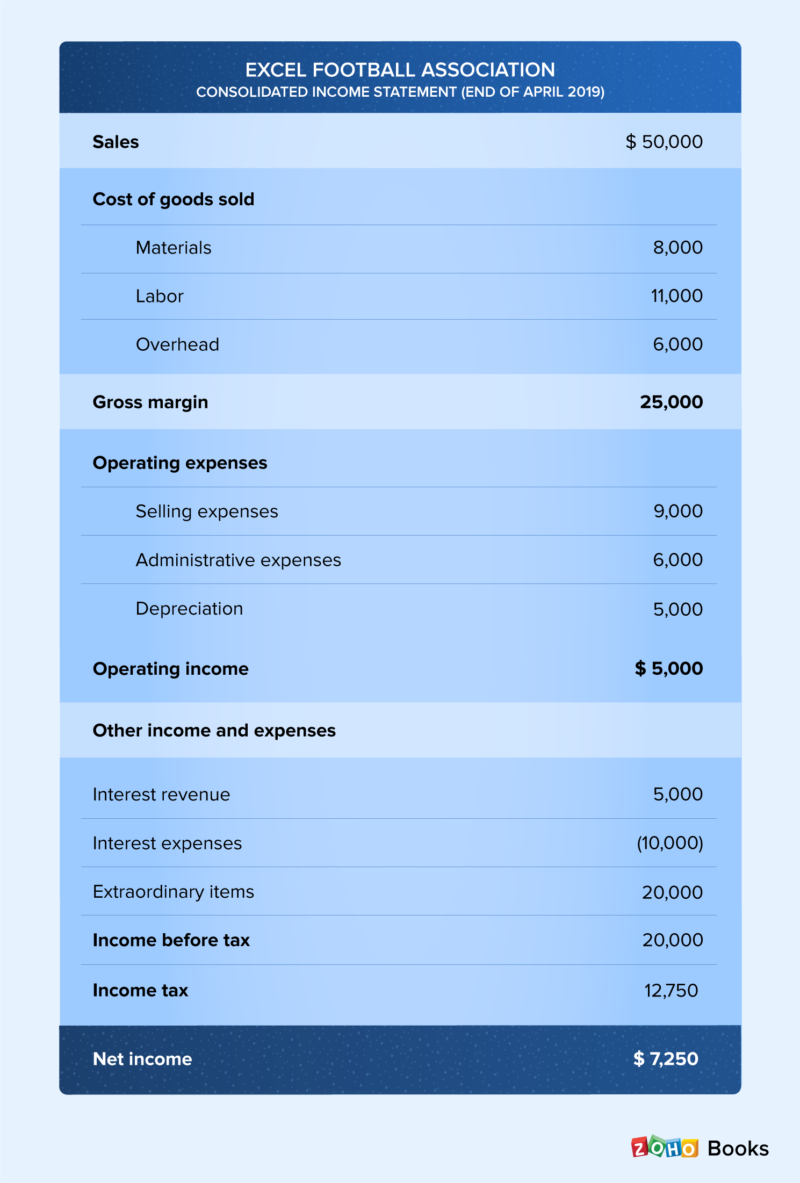
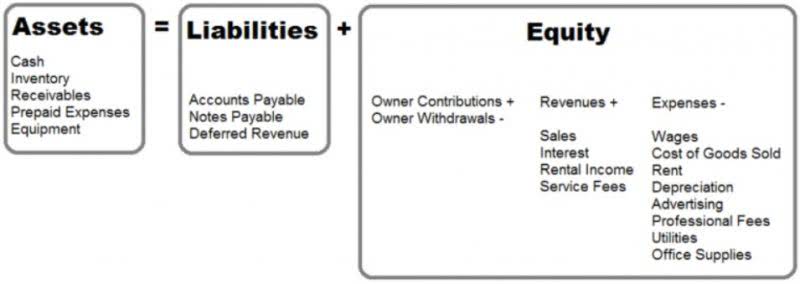
The total costs incurred for a job are divided by the number of units produced. Understanding the company’s organization is an important first step in any costing system. The sticks are dried, and then sent to the packaging department, where the sticks are embossed with the Rock City Percussion logo, inspected, paired, packaged, and shipped to retail outlets such as Guitar Center. In contrast, period costs are not directly related to the production process and are expensed during the period in which they are incurred. This approach matches administrative and other expenses shown on the income statement in the same period in which the company earns income. Material and labor costs that cannot be traced directly to the product produced are included in the overhead costs that are allocated in the production costing process.
Download a free copy of “Preparing Your AP Department For The Future”, to learn:
For example, a construction company, a consulting firm, or a furniture maker might use this system. In a job order costing system, you identify each job or project as a separate cost object and assign costs to it based on the actual resources used. You can use a job cost sheet or a similar document to record the direct materials, direct labor, and applied overheads for each job. This way, you can track the cost and profitability of each job and provide accurate estimates and invoices to your customers. If a company has hybrid production processes that involve both customized jobs and repetitive processes, it may employ job order costing for customized jobs and process costing for standardized or mass-produced items.
Recording Costs in Job Order Costing versus Process Costing
Understanding the full manufacturing process for a product helps with tracking costs. This video on how drumsticks are made shows the production process for drumsticks at one company, starting with the raw wood and ending with packaging. Cost accounting methods help companies determine the cost of production, make informed pricing decisions, allocate resources effectively, identify areas for cost reduction, and improve overall cost control. They provide valuable insights into the cost structure of a company and assist in strategic decision-making. Job order costing is used when goods or services are produced based on specific customer orders or projects.
Process costing requires simpler and less frequent calculations and adjustments to account for the standardization and continuity of the production. You’ll also learn the concepts of conversion costs and equivalent units of production and how to use these for calculating the unit and total cost of items produced using a process costing system. The costing system used typically depends on whether the company can most efficiently and economically trace the costs to the job (favoring job order costing system) or to the production department or batch (favoring a process costing system).
Job order costing vs process costing
So, while it is possible to track the cost of each individual product, the additional information may not be worth the additional expense. One of the main differences between job order costing and process costing is the level of detail and accuracy in costing. Job order costing provides more detailed and accurate information about the costs and profitability of each individual job or project. Process costing provides more aggregated and averaged information about the costs and profitability of the entire production process or product line. Job order costing requires more complex and frequent calculations and adjustments to account for the variations and changes in each job.
Raw materials are stored in the materials storeroom and delivered to the appropriate production department—cutting, painting, or assembly/finishing. The design department uses direct labor to create the design specifications, and, when completed, it sends them to the production department. The production department uses the material and design specifications and adds additional labor to create the sign. The sign is transferred to the finishing department for final materials and labor, before the sign is installed or delivered to the customer. The difference between process costing and job order costing relates to how the costs are assigned to the products.
- Companies that mass produce a product allocate the costs to each department and use process costing.
- So, while it is possible to track the cost of each individual product, the additional information may not be worth the additional expense.
- Each component of the cost of producing the clothing will be tracked as it occurs, thus improving the accuracy of determining the price.
- At this point, Hannah’s company needs to precisely track the material cost and labor costs that are needed to make a batch of shirts.
- In this chapter, you will also learn the terminology used to track costs within the job order cost system and how to segregate and aggregate these costs to determine the costs of production in a job order costing environment.
- The difference between process costing and job order costing relates to how the costs are assigned to the products.
To build your budget, review your income statement and other financial statements for last year. This is crucial to generate job estimates that are as close to your actual cost as possible. You can allocate mileage costs based on the number of miles driven to and from your particular customer’s location for instance.
Job order costing is a costing system used to calculate the costs incurred to complete an individual job or order. In a business that employs a job order costing system, each specific job or order is assigned a unique job number to distinguish it from the others. A third example is found in the chemical industry, such as the manufacture of liquid detergents. In this operation, the process is continuous, and each batch produced is homogeneous in composition and characteristics.
Overhead is applied to each product based on an activity base, which will be explained in Compute a Predetermined Overhead Rate and Apply Overhead to Production. Job order costing is an accounting system that traces the individual costs directly to a final job or service, instead of to the production department. It is used when goods are made to order or when individual costs are easy to trace to individual jobs, assuming that the additional information provides value. In these circumstances, the individual costs are easy to trace to the individual jobs. Even retail companies need to know the cost of the purchased products before the sales price is set. While it seems simple to think of the sales price as the purchase price plus a markup, determining the markup costs needs to be an accurate process in order to ensure the sale price is higher than the product cost.
For example, General Mills uses process costing for its cereal, pasta, baking products, and pet foods. Job order systems are custom orders because the cost of the direct material and direct labor are traced directly to the job being produced. When a company mass produces parts but allows customization on the final product, both systems are used; this is common in auto manufacturing.
Manufacturing overhead is another cost of production, and it is applied to products (job order) or departments (process) based on an appropriate activity base. In a process cost system, costs are maintained by each department, and the method for determining the cost per individual unit is different than in a job order costing system. Rock City Percussion uses a process cost system because the drumsticks are produced in batches, and it is not economically feasible to trace the direct labor or direct material, like hickory, to a specific drumstick.
Process costing handles the same types of manufacturing costs as job order costing. Both systems deal with tracking how manufacturing costs such as direct materials, direct labor, and overhead flow through work-in-process to finished goods and finally, when the goods are sold, to cost of goods sold. As previously mentioned, the two traditional types of costing systems are job order costing and process costing. Each anticipates or determines unit costs of products being manufactured and/or services being provided prior to year-end. This chapter examines job order costing and demonstrates how it differs from process costing. Process Costing and other costing systems (Activity-Based, Variable, and Absorption Costing) are covered in other chapters.
The difference between job costing and process costing
- Look at the expense categories and note each overhead cost and the amount spent before.
- For example, an order comes in to make a planner in a certain color for a large employer to give to all employees.
- At the Peterbilt factory in Denton, Texas, the company can build over \(100,000\) unique versions of their semitrucks without making the same truck twice.
- Although the methods are different, the main difference can be that job costing requires a higher degree of supervision, but process costing does not need so.
- Process costing is used for industries with a vast volume of similar products.
You have just been hired as an accountant at a local manufacturing company. They are a small start-up and are unsure how to enter costs into their accounting system. Having just purchased Quickbooks software, it is time to decide how they get it set up to work most effectively for their needs. The Ultimate Planner is a printed planner designed to make every small business owner’s life just a bit easier.
Equivalent Units
The first method is the weighted-average method, which includes all costs (costs incurred compare and contrast job order and process costing systems. during the current period and costs incurred during the prior period and carried over to the current period). This method is often favored, because in the process cost production method there often is little product left at the end of the period and most has been transferred out. The theory is similar to the FIFO inventory valuation process that you learned about in an earlier chapter. (Since the FIFO process costing method is more complicated than the weighted-average method, the FIFO method is typically covered in more advanced accounting courses.) We will focus on the weighted average method in this course. In process costing, costs are accumulated by production processes or departments rather than by individual jobs.
Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University. It’s best to make an effort to connect each overhead cost to a related or at least somewhat related activity.
The material storage unit stores the types of wood used (hickory, maple, and birch), the tips (nylon and felt), and packaging materials. Regardless of the costing method used (job order costing, process costing, or another method), manufacturing companies are generally similar in their organizational structure and have a similar flow of goods through production. The diagram in Figure 8.1 shows a partial organizational chart for sign manufacturer Dinosaur Vinyl. The CEO has several direct reporting units—Financing, Production, Information Technology, Marketing, Human Resources, and Maintenance—each with a director responsible for several departments. In job order cost production, the costs can be directly traced to the job, and the job cost sheet contains the total expenses for that job.
Batch 1 might be 1,000 solid black masks, while batch 2 is 1,500 red and white striped masks. For example, a company produces a large quantity, but changes or customizes the products before sending them to the client or customers. In this case, both the elements of costing are used; this is also termed a hybrid system.