Additionally, individual taxpayers can include all wages and tips earned as an employee in determining their business income limitation. NetAsset is a user-friendly fixed asset management solution crafted to optimize your company’s entire fixed asset lifecycle, from inception to tax compliance. It saves accounting teams valuable time by simplifying complex calculations and minimizing manual errors, giving you confidence in your financial data. Modifying depreciation methods and schedules manually on spreadsheets can be time-consuming. However, switching to fixed asset management software can help you simplify the process. The first step toward simplifying your fixed asset management is understanding the different depreciation methods and choosing the right one for each asset type.
After all, the private market has topped the stock market in every downturn going back nearly 20 years. There are potential benefits and drawbacks with most anything in the financial space, including straight line depreciation. The calculation simply calls for dividing an asset’s cost, minus its salvage value, by the asset’s useful life. The amount of the asset depreciated over its useful life is referred to as the depreciable cost and is equal to the cost less the salvage value of the asset. You estimate the salvage value will be $2000, so the depreciation expense is now $4000.
- To get a better understanding of how to calculate straight-line depreciation, let’s look at an example.
- To calculate the annual depreciation expense, the cost of the asset is divided by the number of years of its useful life.
- Mastering the straight-line depreciation method is crucial for effective financial health in any business.
- This last step will give you the straight-line depreciation rate per year.
- Useful life refers to the estimated period during which an asset is expected to be useful to its owner.
Create a free account to unlock this Template
Understanding depreciation is crucial for businesses to make informed decisions about their assets. Depreciation can be a complex topic, as there are different types of depreciation and various methods of calculating it. This article will explore the different types of depreciation and the key concepts in depreciation to help readers gain a better understanding of this important accounting concept. Straight line depreciation makes it easier to calculate the expense of a company’s fixed asset. As an accounting process, depreciation spreads a fixed asset’s cost over its useful life, or the period in which it will likely be used. Under the straight line method, the depreciation is the same amount each year.
How to calculate depreciation using the straight-line method
Your asset cost includes anything you spent on getting it ready for use, including shipping or assembly charges. The salvage value is the amount your asset will be worth when it’s no longer useful to your business. A fixed asset having a useful life of 3 years is purchased on 1 January 2013. According to the straight-line method of depreciation, your wood chipper will depreciate by $2,400 every year. Let’s say you own a tree removal service, and you buy a brand-new commercial wood chipper for $15,000 (purchase price). Your tree removal business is such a success that your wood chipper will last for only five years before you need to replace it (useful life).
Moreover, investors can get started with a relatively small amount of capital. Yieldstreet has opportunities across a broad range of asset classes, offering a variety of yields and durations, with minimum investments as low as $10,000. With this method, an asset’s value is uniformly lowered over each period until it reaches its salvage value — the amount an asset is approximated to be worth at the conclusion of its useful life.
- It simplifies allocating the cost of assets over their useful life, ensuring predictable and consistent financial reporting.
- Understanding how much value an asset loses over time allows you to plan for replacements and manage expenses.
- Straight line method is also convenient to use where no reliable estimate can be made regarding the pattern of economic benefits expected to be derived over an asset’s useful life.
- In conclusion, understanding the rules and regulations surrounding depreciation is essential for businesses looking to reduce their taxable income.
Leasehold improvements: A comprehensive guide for accountants
This approach applies a consistent reduction in value period over period. Thanks to its simple calculation, straight-line depreciation is one of the most commonly used deprecation methods. In this post, we will cover all the basics of straight-line depreciation, including the formula to calculate it, its benefits, and alternatives. When disposing of an asset, businesses must calculate any gain or loss for tax purposes by comparing the asset’s adjusted basis—original cost minus accumulated depreciation—with the disposal proceeds.
Claim $20 Off PRO Plus
In this guide, you’ll learn when to use straight-line depreciation, its pros and cons and how to calculate it. From sole traders who need simple solutions to small businesses looking to grow. For the past 52 years, Harold Averkamp (CPA, MBA) hasworked as an accounting supervisor, manager, consultant, university instructor, and innovator in teaching accounting online. For the past 52 years, Harold Averkamp (CPA, MBA) has worked as an accounting supervisor, manager, consultant, university instructor, and innovator in teaching accounting online. Next, you’ll estimate the cost of the salvage value by considering how much the product will be worth at the end of its useful life span. Now that you know what straight-line depreciation is and why it’s important, let’s look at how to calculate it.
The straight-line and accelerated depreciation methods differ in how they allocate an asset’s cost over time. For example, due to rapid technological advancements, a straight line depreciation method may not be suitable for an asset such as a computer. A computer would face larger depreciation expenses in its early useful life and smaller depreciation expenses in the later periods of its useful life, due to the quick obsolescence of older technology. It would be inaccurate to assume a computer would incur the same depreciation expense over its entire useful life.
The units of output method is based on an asset’s consumption of something measurable. It is most likely to be used when tracking machine hours on a machine that has a finite and quantifiable number of machine hours. The depreciation expense calculated by the straight line depreciation method may, therefore, be greater or less than the units of output method in any given year.
Therefore, Company A would depreciate the machine at the amount of $16,000 annually for 5 years. Company A purchases a machine for $100,000 with an estimated salvage value of $20,000 and a useful life of 5 years. Another important provision, Sec. 179(d)(6), states that all members of a controlled group shall be treated as one taxpayer.
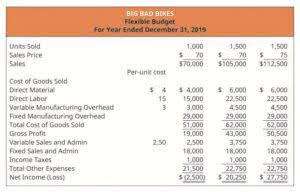
There are various methods of depreciation, including straight-line, declining balance, and sum-of-the-years-digits. The accountant must select the appropriate method based on the nature of the asset and the company’s accounting policies. The income statement is a financial statement that shows the revenue, expenses, and net income of a company over a specific period.
With the straight line depreciation method, the value of an asset is reduced uniformly over each period until it reaches its salvage value. Straight line depreciation is the most commonly used and straightforward depreciation method for allocating the cost of a capital asset. It is calculated by simply dividing the cost of an asset, less its salvage value, by the useful what is straight line depreciation life of the asset. The IRS has specific rules regarding depreciation, and it is important to understand these rules in order to properly calculate and report depreciation on your tax return.
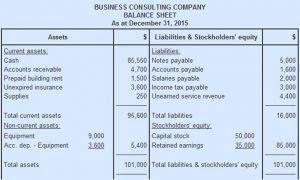
Income Statement
This method is an accelerated depreciation method because more expenses are posted in an asset’s early years, with fewer expenses being posted in later years. The annual depreciation expense is calculated by dividing the depreciable base (asset cost minus salvage value) by the recovery period. For example, an asset with a $50,000 depreciable base and a 10-year recovery period results in a $5,000 annual expense. This straightforward calculation aids in financial planning and tax reporting. In accounting, a lifespan is the estimated time you can use an asset before changing it for a different one.